A Ni-Cr alloy known for its corrosion resistance and high temperature stability
Good corrosion resistance at elevated temperatures

High temperature stability up to 2200°F (982°C)
High strength material with excellent toughness at elevated temperatures
Inconel grades: 600, 601, 625, 686, 718, 725, X750
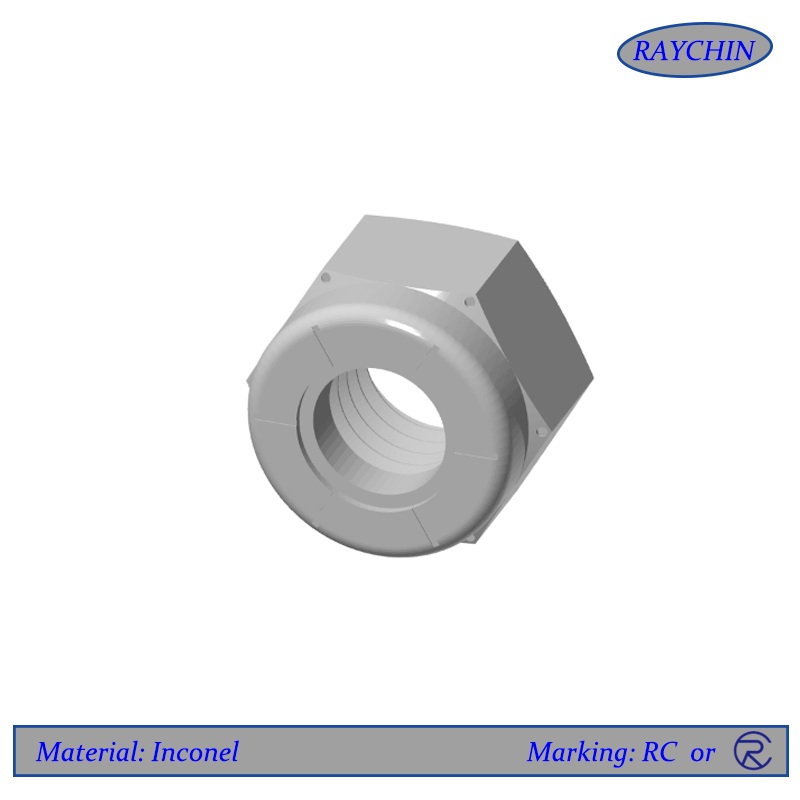
Inconel lock nut features and benefits
Datasheets available on Inconel 625 and Inconel 718
Inconel® lock nuts, like Inconel 600, 601,625, 686, 718 & 725 nuts, are a family of nickel-chromium-molybdenum alloys used for their high strength at elevated temperatures and good corrosion resistance. Because of its high thermal stability, Inconel can be used in service temperatures ranging from cryogenic to 2200°F (982°C). The high alloy content of Inconel lock nuts enable it to withstand a wide variety of severe corrosive environments. In mild environments, such as the atmosphere, sea water, neutral salts, and alkaline media, there is almost no attack to Inconel nuts. In more severe corrosive environments the combination of nickel and chromium provides resistance to oxidizing chemicals, whereas the high nickel and molybdenum contents supply resistance to nonoxidizing environments.
Because Inconel lock nuts offer a good balance of corrosion resistance, temperature stability, toughness and strength they are often a material of choice for chemical processing, aerospace, marine, electronics and oil & gas.
The most commonly used grades of Inconel nickel alloy lock nuts are Inconel 625 and Inconel 718. For more indepth information on these specific grades, visit our Inconel 625 or Inconel 718 fastener pages, or contact one of our engineering experts.
Resources: Inconel Torque Spec
Inconel Locknut Features and Beneifts
An Inconel locknut resists loosening from vibrations and torque. One of the most common styles is a prevailing torque locknut. This kind of Inconel locknut has a prevailing torque feature which deforms elastically, preventing it from freely spinning like a standard nut.
The two most common and reliable forms of prevailing torque locknuts are the flexloc style and the polymer insert lock nut. A Inconel flexloc nut is all-metal in composition with a segmented collar that creates six “locking fingers,” that act as a spring. Inconel polymer insert lock nuts are often referred to as nylon insert locknuts, although various high performance polymers can be used for the screw threads to “bite into.” Both flexlock and polymer insert locknuts are available in both hexagonal and 12 point configurations.
All Metal Flexloc Lock Nut |  Polymer/Nylon Insert Lock Nut Polymer/Nylon Insert Lock Nut |
|
|
Other all metal lock nuts available include the Inconel stover and elliptical styles. Though these styles are often a cheaper initial cost, they are less reliable than the flexloc style. As these styles delivering less prevailing torque cycles and often result in more failures, the flexloc style is a better investment for both reliability and cost savings.
Common Inconel Nut Grades
Inconel 600 (2.4816)
Alloy 600, UNS N06600, is a nickel-chromium alloy with good carburization and oxidation resistance through 2000°F. The alloy has long been used in the heat treating industry and Inconel 600 has useful resistance to dry Cl2 and HCl gases at moderately elevated temperatures.
Inconel 600 Specifications: AMS 5540, AMS 5665, ASME SB 166, ASME SB 167, ASME SB 168, ASTM B 166, ASTM B 167, ASTM B 168, EN 2.4816, UNS N06600, Werkstoff 2.4816, ASTM F2281
Inconel 600 | Ni | Cr | Fe | Mn | Cu | Si | C | S |
Min % | 72 | 14.0 | 6.0 | - | - | - | - | - |
Max % | - | 17.0 | 10.00 | 1.00 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.15 | 0.015 |
Inconel 601 (2.4851)
Inconel 601, UNS N06601, is highly resistant to oxidation through 2200°F even under severe thermal cycling. The alloy has good high temperature strength, and retains its ductility after long service exposure. Inconel 601 alloy has good hot corrosion resistance under oxidizing conditions.
Inconel 601 Specifications: AMS 5715, AMS 5870, ASME SB 167, ASME SB 168, ASTM B 167, ASTM B 168, EN 2.4851, UNS N06601, Werkstoff 2.4851, ASTM F2281
Inconel 601 | Ni | Cr | Fe | Al | Mn | Cu | Si | C | S |
Min % | 58 | 21.0 | - | 1.0 | - | - | - | - | |
Max % | 63 | 25.0 | Bal | 1.7 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.50 | 0.10 | 0.015 |
Inconel 625 (2.4856)
Inconel 625, UNS N06625, EN 2.4856 is the workhorse of the Inconel family and is one of the most common grades. It exhibits high creep-rupture strength and is oxidation resistant to 1800°F (982°C). Inconel 625 has excellent resistance to hot seawater, scrubber environments and reducing acids and this alloy resists a wide range of severely corrosive environments and is especially resistant to pitting and crevice corrosion.
Inconel 625 Specifications: AMS 5666, AMS 5837, ASME SB 443 Gr 1, ASME SB 446 Gr 1, ASTM B 443 Gr 1, ASTM B 446 Gr 1, EN 2.4856, ISO 15156-3, NACE MR0175-3, UNS N06625, Werkstoff 2.4856, ASTM F467 (Nuts), ASTM F468 (Bolts, Screws, Studs)
Inconel 625 | Ni | Cr | Mo | Fe | Nb+Ta | Co | Mn | Si | Al | Ti | C | P | S |
Min % | - | 20.0 | 8.0 | - | 3.15 | 8.0 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
Max % | Bal | 23.0 | 10.0 | 5.0 | 4.15 | 1.0 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.4 | 0.40 | 0.10 | 0.015 | 0.015 |
Inconel 686 (2.4606)
Alloy 686, UNS N06686, is designed for outstanding corrosion resistance in a wide range of severe environments. The alloy is used in the most severe environments encountered in chemical processing, pollution control, pulp and paper production, and treatment of industrial and municipal waste.
Inconel 686 Specifications: ASTM B 462, ASTM B 564 / ASME SB 564, ASTM B 574 / ASME B 574, DIN 17752, DIN 17753, DIN 17754
Inconel 686 | Ni | Cr | Mo | Ti | W | Mn | Si | C | P | S | Fe |
Min % | - | 19.0 | 15.00 | 0.02 | 3.0 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
Max % | Bal | 23.0 | 17.00 | 0.25 | 4.4 | 0.75 | 0.08 | 0.01 | 0.04 | 0.02 | 2.0 |
Inconel 718 (2.4668)
Inconel 718, UNS N07718, EN 2.4668, is the most common grade of the hardenable Inconels. This precipitation-hardened nickel-chromium alloy combines outstanding corrosion resistance and high strength at elevated temperatures. The alloy is a about 2x as strong as Inconel 625 having excellent creep-rupture strength at temperatures to 1300°F (700°C) and usable up to 1800°F (982°C). Inconel 718 is often used in gas turbines, rocket motors, spacecraft, nuclear reactors, pumps, and tooling.
Inconel 718 Specifications: AMS 5596, AMS 5662, AMS 5663, AMS 5832, ASME Case 2222-1, ASME SFA 5.14, ASTM B 637, ASTM B 670, EN 2.4668, GE B50TF14, GE B50TF15, UNS N07718, Werkstoff 2.4668, ASTM F2281
Inconel 718 | Ni+Co | Fe | Cr | Nb+Ta | Mo | Ti | Co | Al | Mn | Si | Cu | C | P | S | B |
Min % | 50 | - | 17.0 | 4.75 | 2.80 | 0.65 | - | 0.20 | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
Max % | 55 | Bal | 21.0 | 5.50 | 3.30 | 1.15 | 1.0 | 0.80 | 0.35 | 0.35 | 0.30 | 0.08 | 0.015 | 0.015 | 0.006 |
Inconel 725
Alloy 725, UNS N07725, nickel-chromium-molybdenum-niobium age-hardenable alloy that has essentially the same corrosion resistance as Inconel 625, but with a strength of that is twice that of annealed Inconel 625. The strength of this alloy is developed by heat treatment to achieve high ductility and toughness. The alloy is resistant to hydrogen embrittlement and stress-corrosion cracking as well.
Inconel 725 | Ni+Co | Cr | Fe | Mo | Nb | Ti | Al | Mn | Si | C | P | S |
Min % | 55 | 19.0 | - | 7.00 | 2.75 | 1.00 | - | - | - | - | - | - |
Max % | 59 | 22.5 | Bal | 9.50 | 4.00 | 1.70 | 0.35 | 0.35 | 0.20 | 0.03 | 0.015 | 0.010 |
Incone X750 (EN 2.4665)
Alloy X-750, UNS N07750, EN 2.4665, is a precipitation hardened alloy known for its corrosion resistance and high temperature oxidation resistance up to temperatures of 1300°F. This alloy is similar to Alloy 600 but made precipitation hadenable with the addition of titanium and aluminium.
Inconel X750 Specifications: ASTM B 637/ASME SB 637; ISO 9723-9725; SAE AMS 5667-5671 and 5747; EN 10269
Inconel 750 | Ni | Cr | Fe | Nb+Ta | Mn | Co | Al | Si | Cu | C | S |
Min % | 70.0 | 14.0 | 5.0 | 0.70 | - | - | 0.40 | - | - | - | - |
Max % | - | 17.0 | 9.0 | 12.0 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 0.50 | 0.50 | 0.08 | 0.01 |
Inconel Frequently Asked Question of the Week
| Inconel 600 or 601 for High Temperature Oxidation Resistance |
Q: For a high temperature oxidation-rich environment which would be better Inconel 600 or 601 bolts? A: For this situation it really depends on the temperature range you are dealing with because both an Inconel 600 bolt and an Inconel 601 bolt offer good oxidation resistance. Inconel 600 can service up to 2000F where Inconel 601 can handle up to 2200F. If you temperatures aren’t that severe, I’d suggest A286 bolts for excellent oxidation resistance. An A286 bolt is known for its high strength, creep resistance and oxidation resistance up to 1300F. |
Mechanical Data
ALLOY 600 - Tensile Data
Temperature (°F) | Ultimate Tensile (ksi) | Yield Strength at 0.2% Offset (ksi) | Elongation % |
Room Temp. | 93.0 | 37. 0 | - |
1000 | 84.0 | 28.5 | |
1200 | 65.0 | 26.5 | |
1400 | 27.5 | 17.0 | |
1600 | 15.0 | 9.0 | |
1800 | 7.5 | 4.0 |
ALLOY 601 - Tensile Data
Temperature (°F) | Ultimate Tensile (ksi) | Yield Strength at 0.2% Offset (ksi) | Elongation % |
Room Temp. | 100.0 | 54.0 | 45.0 |
1000 | 90.0 | 48.0 | 44.0 |
1200 | 60.0 | 41.0 | 45.0 |
1400 | 34.0 | 26.0 | 70.0 |
1600 | 18.0 | 15.0 | 120.0 |
ALLOY 625 - Tensile Data
Temperature (°F) | Ultimate Tensile (ksi) | Yield Strength at 0.2% Offset (ksi) | Elongation % |
Room Temp. | 144.0 | 84.0 | 44.0 |
400 | 134.0 | 66.0 | 45.0 |
600 | 132.0 | 63.0 | 42.5 |
800 | 132.0 | 61.0 | 45.0 |
1000 | 130.0 | 61.0 | 48.0 |
1200 | 119.0 | 60.0 | 34.0 |
1400 | 78.0 | 59.0 | 59.0 |
1600 | 40.0 | 39.0 | 117.0 |
ALLOY 718 - Tensile Data
Temperature (°F) | Ultimate Tensile (ksi) | Yield Strength at 0.2% Offset (ksi) | Elongation % |
Room Temp. | 210.0 | 175.0 | 22.0 |
400 | 138.0 | 163.0 | 20.0 |
800 | 191.0 | 156.0 | 19.0 |
1000 | 185.0 | 155.0 | 18.0 |
1200 | 168.0 | 149.0 | 19.0 |
1400 | 111.0 | 110.0 | 27.0 |
Inconel 718 Heat Treatment Strengths
Ultimate Tensile Strength | Specification |
185ksi min | AMS 5662/5663 ASTM B637 |
220ksi min | AMS 5962 |
PRESSURE - TEMPERATURE RATINGS
FOR ALLOYS C276 / 625 / 825
Nominal Designation | Forgings | Castings | Plates | ||||
54Ni 16Mo 15Cr | 8462 Gr N10276 | B575 Gr. N10276 (1),(2) | |||||
60Ni 22Cr9Mo 3.5Cb | B564GR N 08625 | B443 Gr. N06625 (3), (5) | |||||
42Ni 21.5Cr 3Mo 2.3Cu | 8564 Gr N0S825 | B424 Gr. N08825 (3),(7) | |||||
Working Pressures by Classes, psig | |||||||
Temp F | 150 | 300 | 400 | 600 | 900 | 1500 | 2500 |
20 to 100 | 290 | 750 | 1000 | 1500 | 2250 | 3750 | 6250 |
200 | 250 | 750 | 1000 | 1500 | 2250 | 3750 | 6250 |
300 | 230 | 730 | 370 | 1455 | 2185 | 3640 | 6070 |
400 | 200 | 700 | 930 | 1395 | 2095 | 3490 | 5820 |
500 | 170 | 565 | 885 | 1330 | 1995 | 3325 | 5540 |
600 | 140 | 605 | 805 | 1210 | 1815 | 3025 | 5040 |
650 | 125 | 530 | 785 | 1175 | 1765 | 2940 | 4905 |
700 | 110 | 570 | 755 | 1135 | 1705 | 2840 | 4730 |
750 | 95 | 530 | 710 | 1065 | 1595 | 2660 | 4430 |
800 | 80 | 510 | 675 | 1015 | 1525 | 2540 | 4230 |
850 | 65 | 485 | 650 | 975 | 1450 | 2435 | 4060 |
900 | 50 | 450 | 500 | 900 | 1350 | 2245 | 3745 |
950 | 35 | 385 | 515 | 775 | 1160 | 1930 | 3220 |
1000 | 20 | 365 | 485 | 725 | 1090 | 1820 | 3030 |
1050 | 360 | 480 | 720 | 1080 | 1800 | 3000 | |
1100 | 325 | 430 | 645 | 965 | 1610 | 2685 | |
1150 | 275 | 365 | 550 | 825 | 1370 | 2285 | |
1200 | 205 | 275 | 410 | 615 | 1030 | 1715 | |
1250 | 165 | 220 | 330 | 495 | 825 | 1370 | |
1300 | 120 | 150 | 240 | 360 | 500 | 1000 | |
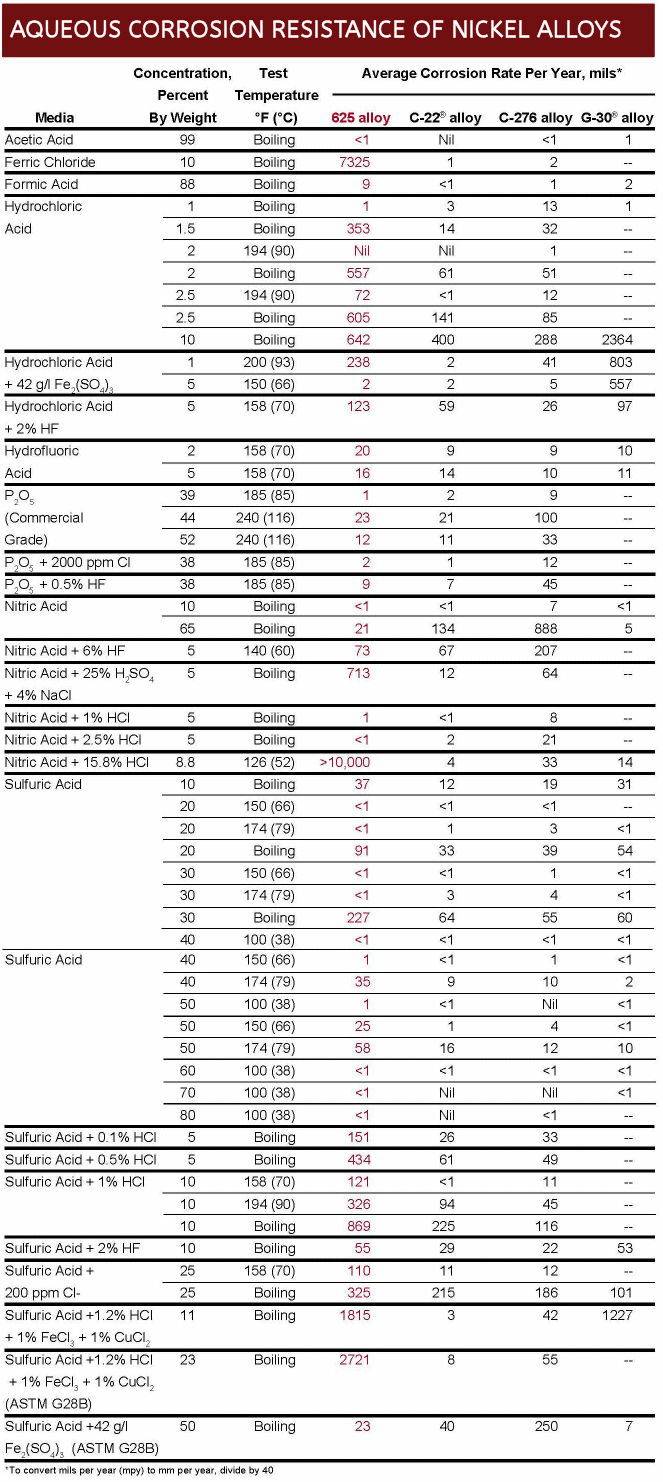
Inconel Corrosion Data